Matplotlib 3次元の散布図#
※記事内に商品プロモーションを含むことがあります。
公開日
この記事では、Matplotlibで3次元の散布図を出力する方法を解説します。2次元の散布図については以下の記事を参照ください。
3次元散布図の基本#
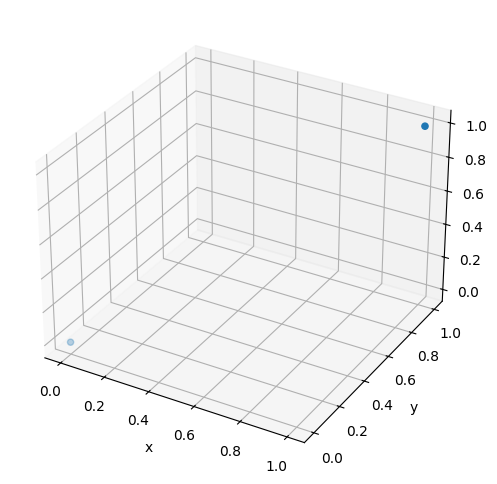
plt.subplots()のsubplot_kwオプションに{'projection': '3d'}という辞書形式データを与えることで、3次元のプロットになります。散布図とするには、さらにax.scatter()メソッドを使います。ax.scatter()に点のx, y, z座標を配列で与えます。以下に2点をプロットした例を示します。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x = [0, 1]
y = [0, 1]
z = [0, 1]
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(6, 6), subplot_kw={'projection': '3d'})
ax.scatter(x, y, z)
ax.set_xlabel("x")
ax.set_ylabel("y")
ax.set_zlabel("z")
plt.show()
Matplotlibの公式サイトによると、以下のようにplt.figure()とfig.add_subplot()を組み合わせた方法が主流のようです。しかし、このサイトでは2次元のグラフと形式を揃えるため、基本的に上の記述方法で解説します。
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(6, 6))
ax = fig.add_subplot(projection='3d')
ax.scatter(x, y, z)
ax.set_xlabel("x")
ax.set_ylabel("y")
ax.set_zlabel("z")
plt.show()

なお、projection='3d'とした場合、axはAxes3DSubplotオブジェクトとなります。
print(type(ax))
<class 'mpl_toolkits.mplot3d.axes3d.Axes3D'>
マーカーの大きさ・色・種類#
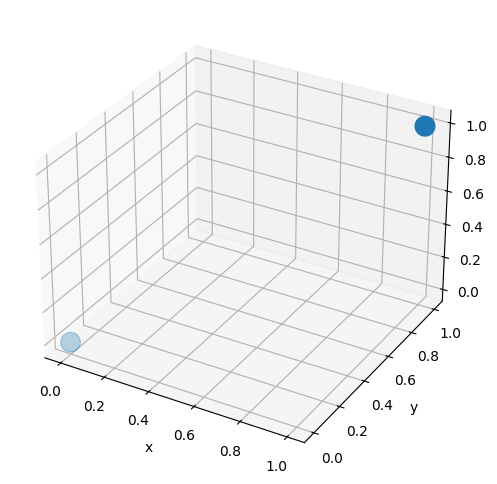
マーカーの大きさはsオプションで指定します。
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(6, 6), subplot_kw={'projection': '3d'})
ax.scatter(x, y, z, s=200)
ax.set_xlabel("x")
ax.set_ylabel("y")
ax.set_zlabel("z")
plt.show()
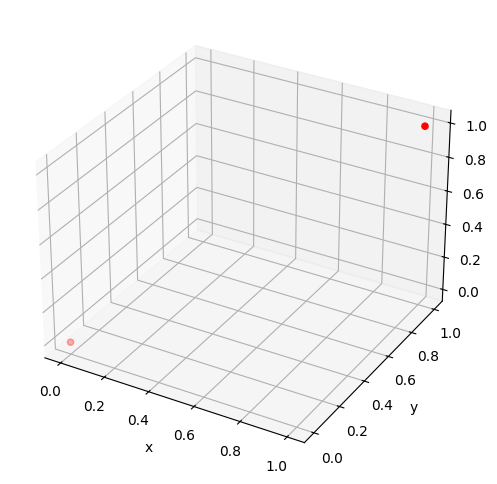
マーカーの色はcオプションで指定します。cオプションの詳細は以下の記事を参考にして下さい。
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(6, 6), subplot_kw={'projection': '3d'})
ax.scatter(x, y, z, c="red")
ax.set_xlabel("x")
ax.set_ylabel("y")
ax.set_zlabel("z")
plt.show()
また、alphaオプションで透明度を変更できます。0から1の範囲を取り、値が小さいほど透明に近づきます。
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(6, 6), subplot_kw={'projection': '3d'})
ax.scatter(x, y, z, alpha=0.5)
ax.set_xlabel("x")
ax.set_ylabel("y")
ax.set_zlabel("z")
plt.show()
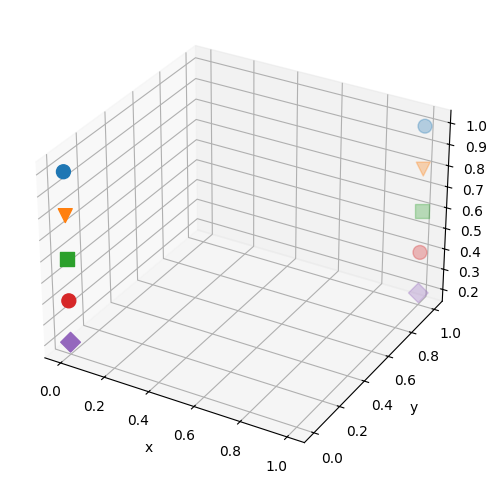
マーカーの種類はmarkerオプションで指定します。
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(6, 6), subplot_kw={'projection': '3d'})
ax.scatter(x, y, [1.0, 1.0], s=100, marker="o")
ax.scatter(x, y, [0.8, 0.8], s=100, marker="v")
ax.scatter(x, y, [0.6, 0.6], s=100, marker="s")
ax.scatter(x, y, [0.4, 0.4], s=100, marker="o")
ax.scatter(x, y, [0.2, 0.2], s=100, marker="D")
ax.set_xlabel("x")
ax.set_ylabel("y")
ax.set_zlabel("z")
plt.show()
カラーマップの指定#
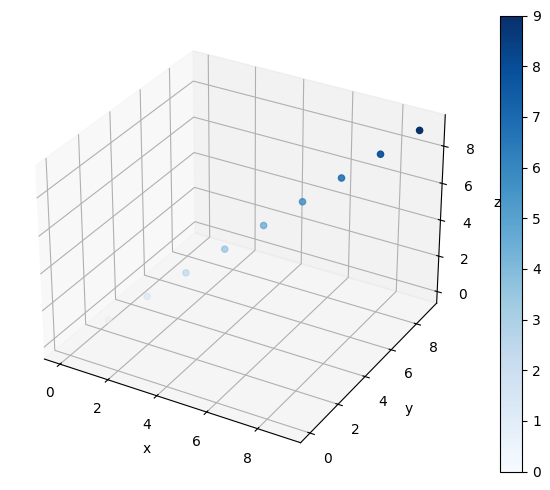
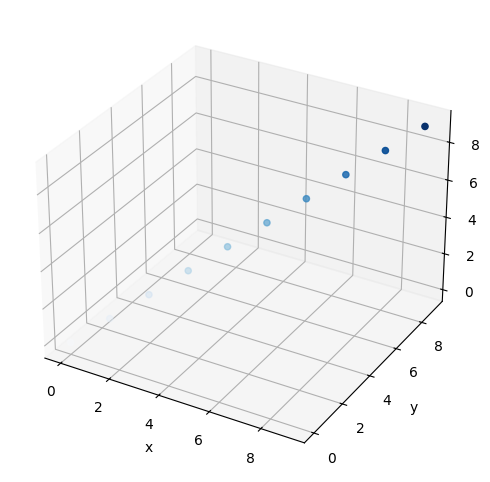
散布図の各点の色を、値に合わせて指定できます。cに値を、cmapにカラーマップを指定します。
以下の例では、Bluesというカラーマップを使用しています。c1の値が大きいほど、点の青色が濃くなっています。
x1 = range(10)
y1 = range(10)
z1 = range(10)
c1 = range(10)
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(6, 6), subplot_kw={'projection': '3d'})
ax.scatter(x1, y1, z1, c=c1, cmap="Blues")
ax.set_xlabel("x")
ax.set_ylabel("y")
ax.set_zlabel("z")
plt.show()
指定可能なカラーマップについては、以下のページを参照下さい。
カラーバーを表示する場合、plt.colorbarを使用します。ax.scatterの戻り値はPathCollectionというクラスのオブジェクトです。これをplt.colorbarの最初の引数とします。また、axオプションにカラーバーを表示するグラフ(ここではax)を指定します。
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(7, 5), subplot_kw={'projection': '3d'})
mappable = ax.scatter(x1, y1, z1, c=c1, cmap="Blues")
plt.colorbar(mappable, ax=ax)
ax.set_xlabel("x")
ax.set_ylabel("y")
ax.set_zlabel("z")
fig.tight_layout()
plt.show()